There are 4 analog input channels on the Main connector, that share the same external pin with digital channels. The MCU can select one of two external input ranges:
- Range = High (0 – 32 Volts)
- Range = Low (0 – 5 Volts)
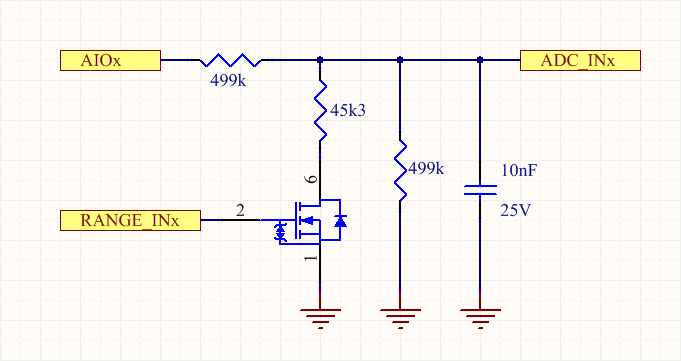
Here below the simplified schematic of each analog channel:
Here is an example Arduino sketch that reads analog inputs AIO1 and AIO2 and prints out the measured voltage:
void setup() { // Open and wait serial terminal Serial.begin(115200); while (!Serial); // Configure analog input range pinMode(PIN_C_IN1_PD, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(PIN_C_IN1_PD, LOW); // Range 0-5V pinMode(PIN_C_IN2_PD, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(PIN_C_IN2_PD, HIGH); // Range 0-32V // Set ADC resolution analogReadResolution(12); } void loop() { // Read analog channels and convert to Volts float vin1 = analogRead(AIN_EXT_IN1) * ANALOG_SCALE_LOW * ANALOG_VREF / 4095.0f; Serial.print("AIO1 (V): "); Serial.println(vin1); float vin2 = analogRead(AIN_EXT_IN2) * ANALOG_SCALE * ANALOG_VREF / 4095.0f; Serial.print("AIO2 (V): "); Serial.println(vin2); delay(1000); }
The same example with Zerynth:
from fortebit.polaris import polaris polaris.init() while True: print("AIO1 (V):", polaris.readAnalogInputVoltage(0, LOW)) print("AIO2 (V):", polaris.readAnalogInputVoltage(1, HIGH)) sleep(1000)
